You’ve built what you believe is a foolproof trading system, but it’s hemorrhaging money instead of profits. You’re not alone—most traders make critical mistakes that sabotage their strategies before they even begin. The good news? These errors are predictable and preventable once you know what to look for. Let’s examine the most common pitfalls that turn promising trading systems into costly failures, and how you can avoid them.
Why Most Algorithmic Trading Systems Fail
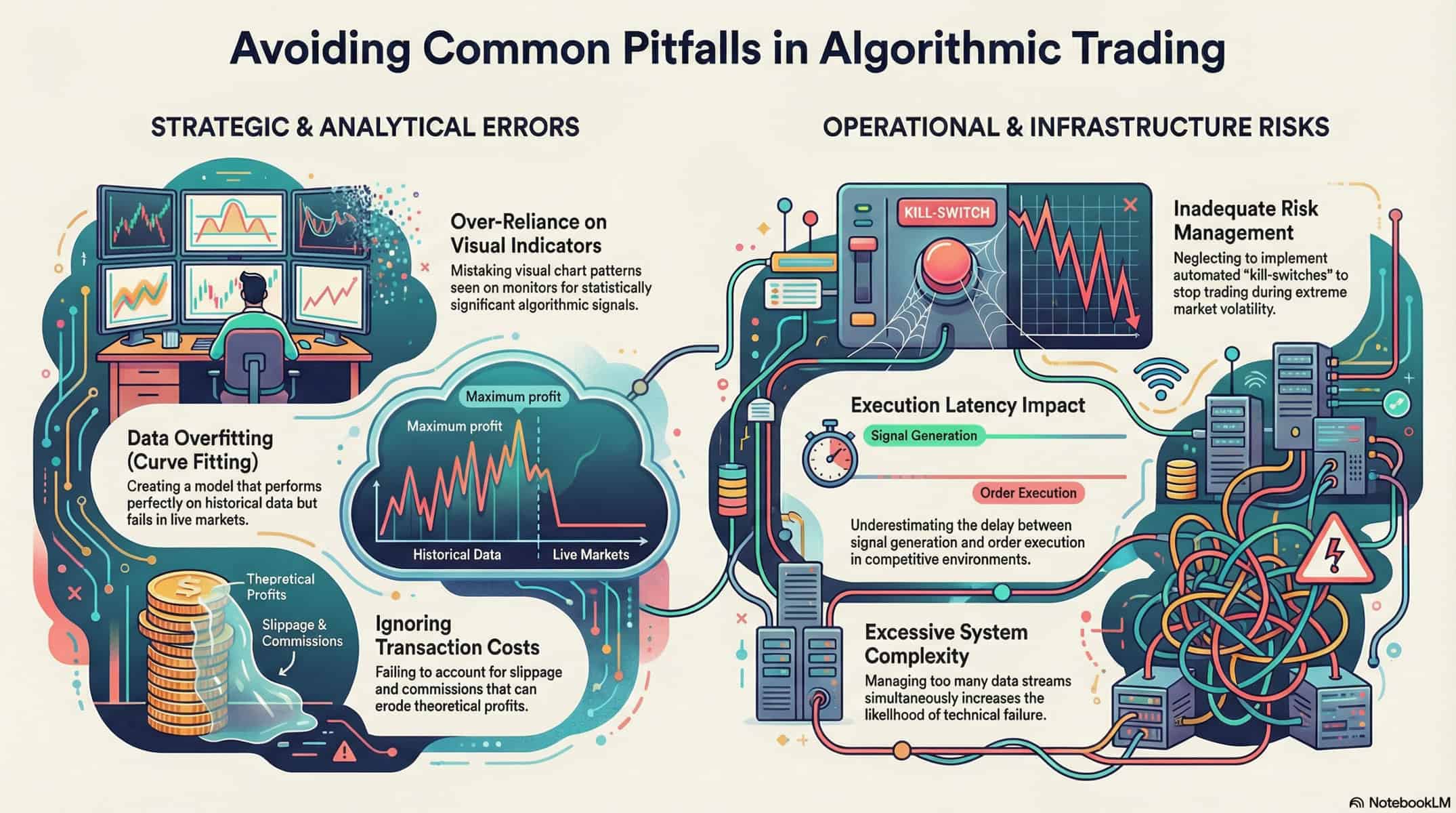
If you’ve ever wondered why most trading systems fail, the answer often lies in how they’re built and tested. Curve fitting occurs when models are overly optimized for historical data, capturing random noise instead of real market patterns. A solid strategy often delivers profit factors between 1.5 and 2.0, while Sharpe ratios above 3.0 might signal curve fitting. Weak risk management is one of the costliest mistakes, as missing or misconfigured stop-loss orders can turn small losses into major setbacks. Ignoring transaction costs and slippage can drastically reduce a strategy’s profitability, sometimes by more than 50%. Testing a strategy only on current NIFTY50 stocks can show inflated returns, while including previously part of the index often reveals more realistic performance. These pitfalls can sabotage even the most promising trading systems.
The Overfitting Trap: When Past Data Misleads Your Strategy
When a trading model becomes excessively aligned with historical data, it can erroneously interpret random fluctuations as genuine trends. You might think you’ve uncovered a winning strategy, but in reality, you’ve just memorized noise.
This overfitting occurs when your model adjusts to every minor detail in past data, including random market movements that won’t repeat.
Consider a model optimized on five years of S&P 500 data. It performs brilliantly on historical prices but fails miserably in live trading. Why? Because it’s learned to recognize patterns specific to that exact dataset. Real markets are dynamic and constantly evolving. What worked yesterday often fails tomorrow.
To avoid overfitting, use techniques like cross-validation and out-of-sample testing. Limit the number of parameters in your model. Remember, simplicity often outperforms complexity in trading. Focus on resilient strategies that capture fundamental market dynamics rather than perfect historical fit.
Risk Management Failures That Destroy Trading Accounts
You might think your strategy runs flawlessly, but without proper risk controls, one bad trade can wipe out your account. Ignoring stop-losses or sizing positions too aggressively leaves you exposed to devastating drawdowns.
Even small transaction costs compound over time, silently eroding your returns if you don’t account for them.
Inadequate Stop-Loss Implementation
Without a solid stop-loss strategy, even the most promising trading system can crumble. You might think you’ve got a winning formula, but without proper risk controls, a few bad trades can wipe out your account.
Setting up automated stop-loss orders is vital to protect your portfolio from excessive losses. Don’t underestimate the power of limiting individual positions to around 1-2% of your total portfolio value. This simple rule can spread risk and prevent overexposure.
Ignoring transaction costs and slippage is another common pitfall. These factors can drastically reduce your strategy’s profitability, sometimes slashing returns by more than 50%. You need to factor these into your calculations to get a realistic view of your potential gains. Risk management failures are among the costliest mistakes in algorithmic trading, often leading to account blowouts.
Excessive Position Sizing Risks
Position sizing is a silent killer in algorithmic trading. Many traders overlook this critical aspect, focusing instead on strategy development.
You might think bigger positions mean bigger profits, but this mindset can quickly lead to disaster. Risk management failures often result in drawdowns exceeding 50% of a trading account. When this happens, recovery becomes nearly impossible without drastic measures.
The 1-2% rule exists for a reason. It advises risking no more than 1-2% of total capital on any single trade. This guideline preserves long-term sustainability and protects against catastrophic losses.
Automated systems without proper risk controls can execute oversized trades during volatile markets. These systems amplify losses exponentially, turning a bad day into a financial nightmare.
Leverage adds another layer of risk to position sizing. Failing to account for leverage can lead to margin calls and account liquidation. In highly leveraged trading environments, this risk becomes even more pronounced. You must always consider the potential impact of leverage on your position sizes.
Ignoring Transaction Costs Impact
Many traders overlook transaction costs, assuming they’re negligible in the grand scheme of trading profits. You’ll quickly learn this mistake can destroy even the most promising strategies.
Those small fees and slippage add up faster than you think, especially when you’re making thousands of trades. Your backtest might show a 15% annual return, but after accounting for real-world transaction costs, you could be looking at just 5%.
High-frequency strategies are particularly vulnerable. With thin profit margins per trade, commission fees and slippage can eat away your returns. A seemingly profitable strategy making $0.50 per trade might lose money after accounting for $0.30 in transaction costs.
You need to build realistic cost estimates into your trading model from day one, or you’ll watch your account balance shrink despite what your backtest promised.
Backtesting Mistakes That Give False Confidence
You might think your model works perfectly after backtesting, but tailoring historical data too closely can give you false confidence. This happens when your strategy is too finely tuned to past data, capturing random noise instead of real market patterns. A good rule of thumb is to aim for a profit factor between 1.5 and 2.0, and a Sharpe ratio above 3.0 might indicate over-optimization.
Overfitting Historical Data
When traders fine-tune their models to match historical data perfectly, they often fall into the trap of over-adaptation. This happens when models capture random noise instead of real market patterns. A solid strategy typically delivers profit factors between 1.5 and 2.0. Sharpe ratios above 3.0 might signal over-adaptation.
- Focus on understanding market behavior, not excessive parameter tweaking
- Avoid complex models that excel on past data but fail live
- Test strategies on out-of-sample data regularly
- Build resilient approaches that work across different market environments
Over-adaptation gives false confidence. You might see impressive backtest results, but your strategy could crumble in live trading. Instead of chasing perfect historical performance, aim for strategies that capture genuine market patterns. This approach leads to more reliable results in real-world conditions.
Ignoring Market Conditions
Market conditions change constantly, yet many traders test their strategies using only one type of market environment. You might run backtests during a bull market and assume your system will perform well in all conditions. This assumption can lead to disaster when markets shift. Different market regimes require different approaches.
Consider testing your strategy across various market conditions. Include periods of high volatility, low volatility, trending markets, and ranging markets. For example, test your system during the 2008 financial crisis and the 2020 COVID-19 market crash. These extreme events reveal weaknesses you mightn’t see in normal times.
Don’t forget to account for changing correlations between assets. What worked when stocks and bonds moved inversely might fail when they suddenly correlate. By testing across diverse conditions, you’ll build more resilient systems that can handle whatever the market throws at them.
Bad Data: The Hidden Cause of Trading Losses
Poor data quality quietly undermines even the most sophisticated trading algorithms. You might think your system is flawless, but garbage in means garbage out.
Cross-checking multiple trustworthy data sources helps improve data reliability and catch inconsistencies before they cost you money. Setting up real-time validation checks is critical for identifying unusual data patterns that could impact trading performance.
Regular maintenance and timely updates of data sources are essential to guarantee the continued effectiveness of trading algorithms. Accurate data is the backbone of both backtesting and live trading, directly affecting the success of algorithmic strategies.
Don’t let bad data be the hidden cause of your trading losses. Take control of your data quality now.
Why Simple Beats Complex in Algorithmic Trading
You’ll often find that simpler trading strategies outperform complex ones over time. Overly complex models can be harder to maintain and more prone to hidden errors. Simple strategies with clear rules are easier to monitor and troubleshoot. Documenting all parameters and their reasoning helps in understanding and improving the system.
Testing performance across various market conditions validates the strategy is resilient. Prioritizing simplicity reduces the risk of excessive customization and improves long-term reliability. When you keep things straightforward, you’re less likely to encounter unexpected issues. Complex systems might seem impressive, but they often introduce more problems than they solve. By focusing on simplicity, you can create a more stable and effective trading approach. Remember, in algorithmic trading, less is often more.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Detect Overfitting in My Trading Strategy?
You can detect overfitting by backtesting your strategy on out-of-sample data, using walk-forward analysis, and monitoring performance metrics like Sharpe ratio and drawdown. Regularly validate and adjust your model.
What Are the Best Risk Management Techniques for Algorithmic Trading?
To manage risks in automated trading, you should diversify your portfolio, use stop-loss orders, limit borrowing, and regularly monitor and adjust your algorithms.
How Often Should I Update My Backtesting Data?
You should update your backtesting data regularly, ideally monthly or quarterly, to guarantee your strategies remain effective and adapt to changing market conditions. This helps maintain accuracy and relevance in your trading decisions.
What Data Sources Are Most Reliable for Algorithmic Trading?
For reliable algorithmic trading data, you should prioritize sources like Bloomberg, Reuters, and Quandl. These platforms offer accurate, real-time market data that can enhance your trading strategies and decision-making processes.
How Do I Simplify My Trading Algorithm Without Losing Effectiveness?
To simplify your trading method without losing effectiveness, focus on removing unnecessary complexity, streamlining code, and optimizing parameters. Prioritize essential features and avoid overfitting. Test thoroughly to guarantee reliability and performance.
Conclusion
Avoid these common mistakes, and you’ll improve your trading results. Poor backtesting ruins strategies. Bad data leads to false confidence. Poor risk management destroys accounts. Keep your approach simple and test thoroughly. Validate regularly. Document everything. These steps separate successful traders from the rest. Focus on execution, not complexity.

Leave a Reply